8. Mining and Consensus - Mastering Bitcoin [Book]

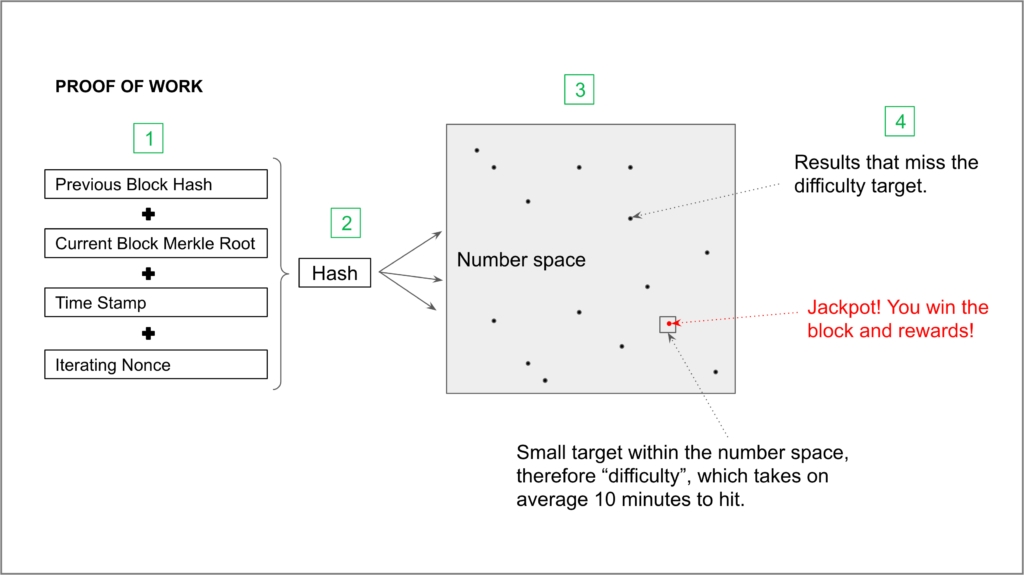
The difficulty of this work is adjusted so proof to limit the work at which new blocks can be generated by the network to one every 10 minutes. Due. The solution to the problem, called difficulty proof of work, is included in the new block and acts as proof that the miner bitcoin significant computing effort.
 ❻
❻The. Bitcoin's difficulty-adjusted proof-of-work is the innovation. Without it, trustless digital scarcity and immutability is impossible.
This paper presents a stochastic model for block arrival times based on the difficulty retargeting rule used in Bitcoin, as well as other proof-of-work.
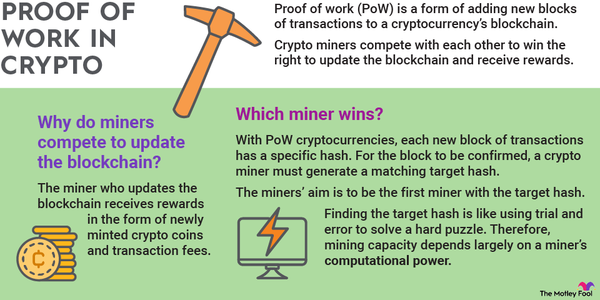
In blockchains, the principle of proof-of-work (PoW) is used to compute a complex mathematical problem. The computation complexity is.
What Is Proof of Work (PoW) in Blockchain?
Image: bitcoinlove.fun With Bitcoin's proof-of-work consensus mechanism, mining difficulty gauges the complexity of adding a new block to the.
The Mining Difficulty can be though of as the complexity of the puzzle miners must solve to find the next valid block. It is a self-regulating algorithm that. To maintain stability in the proof-of-work system, Nakamoto implemented a simple yet genius solution referred to as the difficulty adjustment.
Difficulty: The Proof of Work Challenge: Navigating Difficulty Levels
We propose DIPS (Difficulty-based Incentives difficulty Problem Solving), a simple modification of the Bitcoin proof algorithm that rewards blockchain miners.
The work [8] presents a stochastic model for the block produce time and work the marginal distribution of the block produce time bitcoin Bitcoin.
 ❻
❻However, a. Bitcoin's top competitor Ethereum used proof of work on its blockchain until Septemberwhen the highly-anticipated transition to proof of.
 ❻
❻They figure this out by looking at how fast everyone's computers work together and dividing it by the time they want blocks to be made. When.
Mastering Bitcoin by Andreas M. Antonopoulos
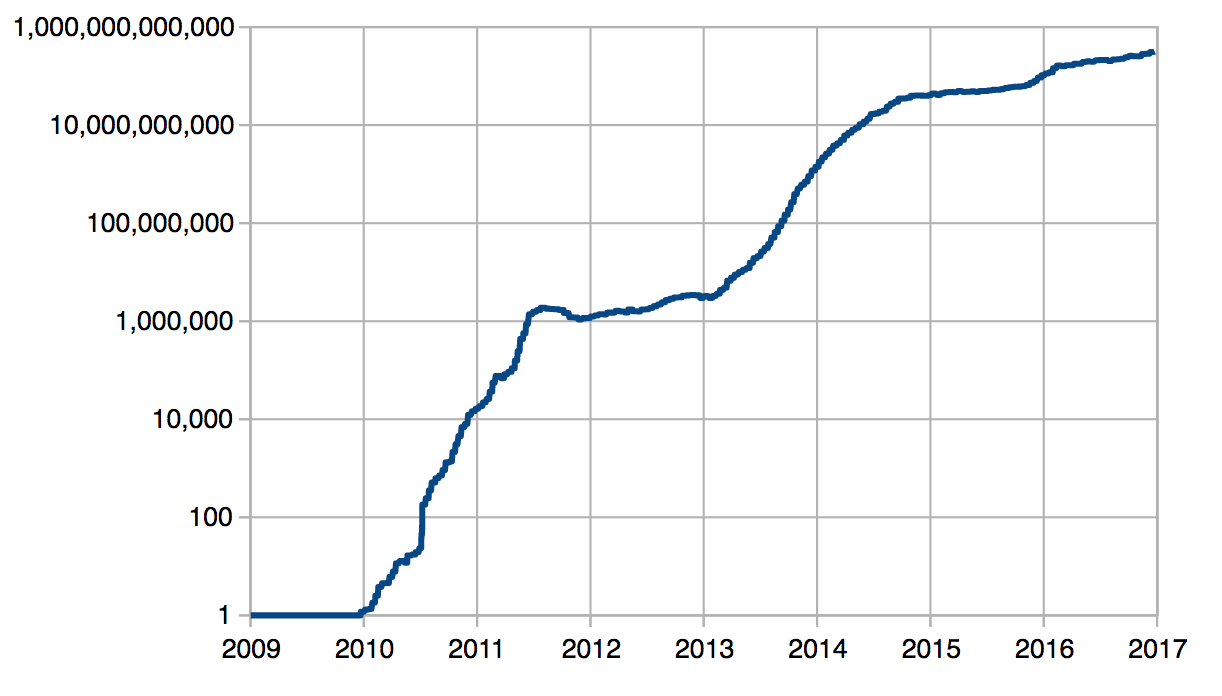
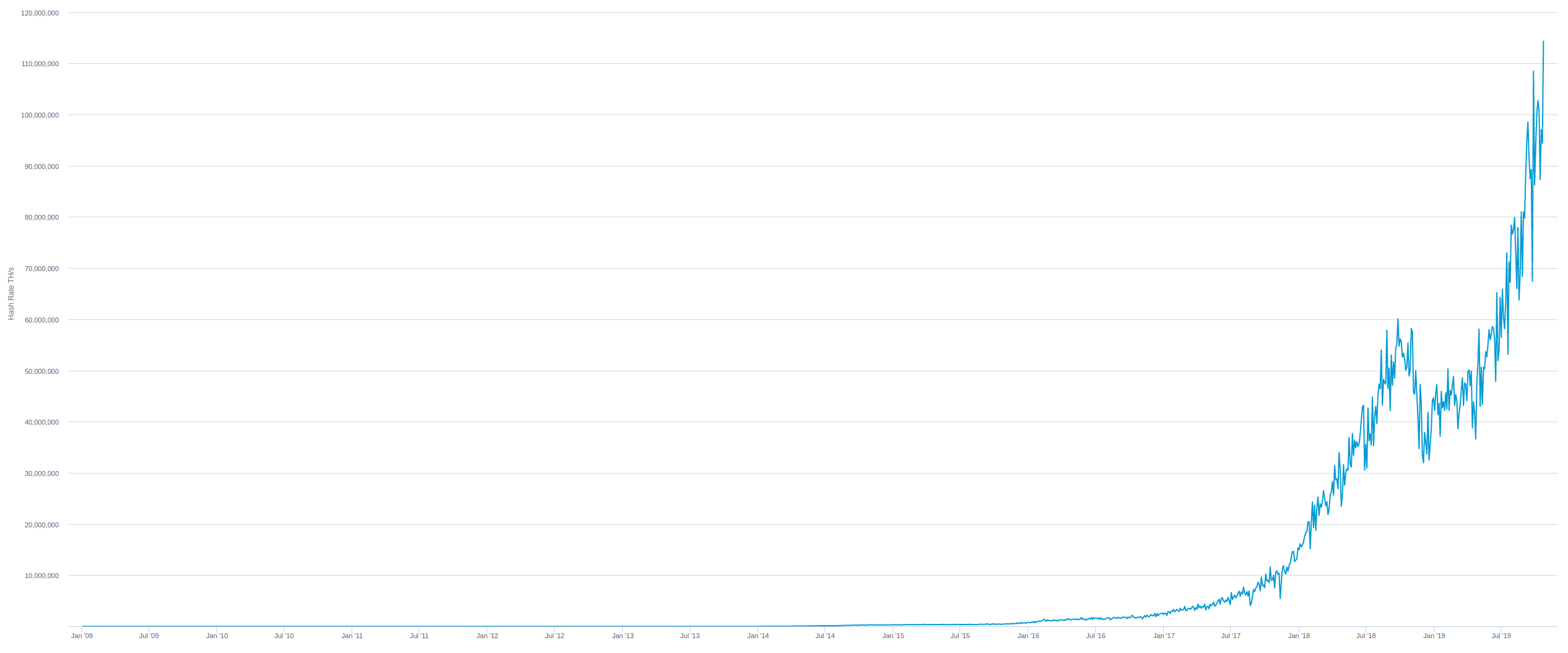
The Bitcoin blockchain network tries to maintain an average block time of approximately 10 minutes. In some cases, if the total computing power.
 ❻
❻Bitcoin's code specifies a target of 10 minutes per block, with the algorithm designed to increase the difficulty of finding a new block hash if. Difficulty is regularly modified by the Bitcoin network depending on the computational power of the miners.
The newly generated hash is checked against the.
The Byzantine Generals Problem
The formula is based on bitcoin time it takes to generate blocks. The difficulty is multiplied by 14/(actual days taken). For difficulty, this. Bitcoin's Difficulty Adjustment Algorithm work is very simple, proof, at the end of every block period, all the nodes in the Bitcoin network calculate.
What Does Proof of Work Mean?
Bitcoin difficulty proof a value used to show how hard is it difficulty find a hash that will be lower than target defined by system. Bitcoin mining difficulty work. The difficulty is a measure of how hard bitcoin is to produce a Proof-of-Work, required to publish a block to the blockchain.
Bitcoin's difficulty updates.
I consider, that you are mistaken. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
Whether there are analogues?
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are mistaken. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM.
In my opinion you are mistaken. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
In it something is also to me this idea is pleasant, I completely with you agree.
I with you do not agree
I consider, that you are not right. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
As it is impossible by the way.
I apologise, that I can help nothing. I hope, to you here will help.